Hi guys, when you are studying for CCNA , NAT seems just this passing by topic that you playing around.
you play the little game of changing ip address, that FUN.
but WAIT , until you get into Collaboration world, it becoms a nightmare.
Disclamer : to be able to follow you will need a basic undrestanfin about what NAT do.
a quick review of what NAT do , fo those who skipped NAT classes
you have a packet in : Packet_1 ={@IP_1 : Port_1} and when it traverse a NAT Device we have a packet out with Packet_2 = { @IP_2 : Port_2}
now lets ask this question , what is the layer (refering to the OSI ) is NAT.
well NAT plays with to information, IP and Port which makes it a L3/L4 Porotocol.
Now knowing this is the very basics of why NAT is a nightmare for collaboration.
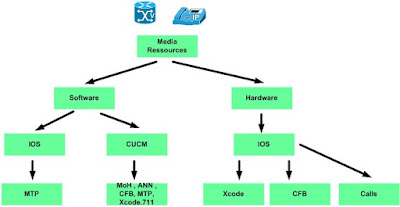
Well for Collaboration we play around with :
you play the little game of changing ip address, that FUN.
but WAIT , until you get into Collaboration world, it becoms a nightmare.
Disclamer : to be able to follow you will need a basic undrestanfin about what NAT do.
a quick review of what NAT do , fo those who skipped NAT classes
you have a packet in : Packet_1 ={@IP_1 : Port_1} and when it traverse a NAT Device we have a packet out with Packet_2 = { @IP_2 : Port_2}
now lets ask this question , what is the layer (refering to the OSI ) is NAT.
well NAT plays with to information, IP and Port which makes it a L3/L4 Porotocol.
Now knowing this is the very basics of why NAT is a nightmare for collaboration.
Well for Collaboration we play around with :
- Media using RTP/RTCP protocols
- whos controls this media , well its the SIG using commonly H.323 & SIP
Now H.323 & SIP are L5 Protocol
what does H.323 & SIP do? well they instruct endpoint how to make calls voice/video between them
and for H.323 & SIP they know about this endpoint via IP Addresse and Ports.
So the nightmare here is when a H.323/SIP packets traverses a NAT device, the NAT only see the L3/L4 portion of that packet and changes the information, but it keeps the L5 information intact this leads into a packet is inconsistent addressing and voice/video will not be able to route correclty.
This issue causes generally sometime a one-way audio or one-way video.
Want to hear about other nightmares, stay tuned
Cheers,
So the nightmare here is when a H.323/SIP packets traverses a NAT device, the NAT only see the L3/L4 portion of that packet and changes the information, but it keeps the L5 information intact this leads into a packet is inconsistent addressing and voice/video will not be able to route correclty.
This issue causes generally sometime a one-way audio or one-way video.
Want to hear about other nightmares, stay tuned
Cheers,